RFID and NFC are two technologies that often get mixed up because they work in similar ways. While it’s not entirely wrong to confuse them, there are still key differences between the two.
NFC vs. RFID: The difference between NFC and RFID
RFID and NFC are both technologies that allow devices to communicate wirelessly. Simply put, NFC is a type of RFID. The biggest difference between them is how far they can communicate.
RFID can send and receive signals over long distances—sometimes up to 100 meters or more, especially if the RFID tag has its own battery (known as an active tag). In contrast, NFC has a much shorter range, typically working within 0 to 5 cm, and at most, up to 20 cm in ideal conditions.
Another key difference is the frequency they use. RFID operates across a range of frequencies, while NFC is limited to a specific high frequency of 13.56 MHz.
RFID definition and applications
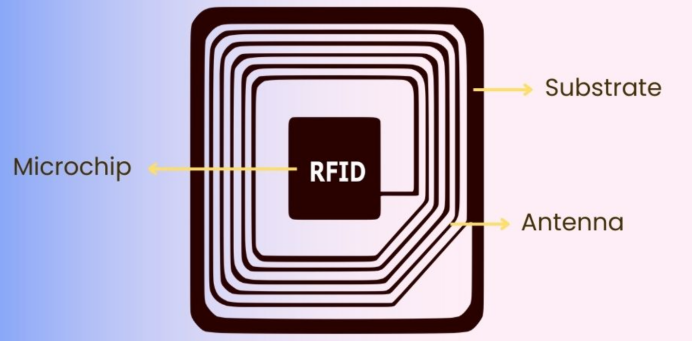
Definition of RFID: RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify objects, animals, or people.
How it works is pretty straightforward:
An RFID system has two main parts – a tag and a reader. The RFID tag contains a small chip that stores information, and when it gets near an RFID reader (a device that sends out radio signals), the tag sends back the stored information. This is like how a barcode works but with radio waves instead of scanning with light.
RFID Applications
RFID technology is now widely used in both public and private sectors. A common example is electronic toll collection, which makes life easier for countless drivers by automating road toll payments.
RFID is also becoming a key part of the Internet of Things (IoT). Many industries, such as energy, transportation, and retail, rely on this technology for various uses:
- In the energy sector, RFID helps maintain installations.
- It can identify multiple items from a distance all at once, unlike barcodes or QR codes.
- It speeds up stock management and allows real-time tracking of inventory.
- It ensures product traceability, which is especially important in industries like food production.
- It improves logistics by managing both transport vehicles and the goods being shipped.
The possibilities for RFID applications are almost endless, especially when combined with IoT—it’s really only limited by your imagination!
NFC Definition and Applications

Definition of NFC:NFC (Near Field Communication) is a wireless communication technology that allows devices to exchange data over short distances, typically within a range of about 4 centimeters (1.6 inches). It’s commonly used for contactless payments, such as tapping a smartphone or credit card on a payment terminal, as well as for tasks like pairing devices, sharing files, or accessing information from NFC tags.
NFC operates at a high frequency (13.56 MHz) and is a subset of RFID technology, but with a much shorter range. It’s popular because of its convenience, speed, and security in applications like mobile payments, public transport cards, and smart access control systems.
How NFC Works
NFC (Near Field Communication) works with two parts: a reader (the terminal) and a receiver (a tag or label). They talk to each other using electromagnetic fields but only over very short distances. A common example of this is when you use contactless payment with a bank card—it’s secure because of the limited range.
NFC Applications
NFC is most commonly used in smartphones. For years now, people have been using their phones to make contactless payments, validate train tickets, and more. Beyond that, NFC has a ton of other uses, both for personal and business needs.
Both NFC and RFID technologies have lots of advantages for users and businesses alike. These benefits grow even more if the devices are connected to the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing for secure data transfers, long-distance communication, and access to extra cloud-based data. If you need help deciding when to use NFC instead of RFID, feel free to reach out, and we’ll guide you through the process.



