I remember the first time I used a fingerprint scanner. It was a simple, traditional sensor on my phone. At that time, I didn’t really think about the differences between various types of fingerprint scanning technologies. But over time, I’ve learned that traditional fingerprint scanners and biometric fingerprint scanners are actually very different in terms of technology and security. So, which one is the better choice for you?
What is the difference between traditional fingerprint scanners and biometric fingerprint scanners?
Traditional fingerprint scanners rely on basic technology to scan fingerprints, whereas biometric fingerprint scanners use advanced features like ultrasonic or 3D imaging to capture more detailed data. Biometric scanners offer better security and accuracy, making them more reliable in sensitive environments.
I’ve used both types of scanners, and I can tell you from personal experience, the difference is noticeable. When I switched to a biometric scanner, I felt that extra layer of security. The traditional scanner often failed to recognize my fingerprint under certain conditions, like if my hands were slightly wet or dirty. That’s not the case with biometric scanners.
What Makes Traditional Fingerprint Scanners Different?
Traditional fingerprint scanners have been around for a while. But what makes them so different from the newer biometric models?
Traditional fingerprint scanners capture only the outer details of a fingerprint, making them less accurate and more prone to errors.
I remember feeling frustrated with my first traditional scanner. It took several tries to get a clean scan, especially when my finger wasn’t positioned just right. Over time, these scanners have gotten better, but they’re still based on older technology that can struggle with things like dirt or damaged fingerprints.
How Traditional Fingerprint Scanners Work
Traditional fingerprint scanners rely on optical sensors or capacitive sensors to capture an image of your fingerprint. Optical sensors shine light onto your fingerprint and capture the reflection, while capacitive sensors use electrical charges to create a digital image of your fingerprint.
| Traditional Fingerprint Scanner | Biometric Fingerprint Scanner |
| Uses basic optical or capacitive sensors | Uses advanced ultrasonic or 3D sensors |
| Prone to errors, especially in challenging conditions | Offers high accuracy in various environments |
| Can be fooled by fake fingerprints | Highly secure, difficult to spoof |
What Makes Biometric Fingerprint Scanners Different?
So, what exactly makes biometric fingerprint scanners stand out? Let’s take a closer look at how they work.
Biometric fingerprint scanners analyze deeper features of your fingerprint, such as ridge patterns and sweat pores, making them more secure and accurate.
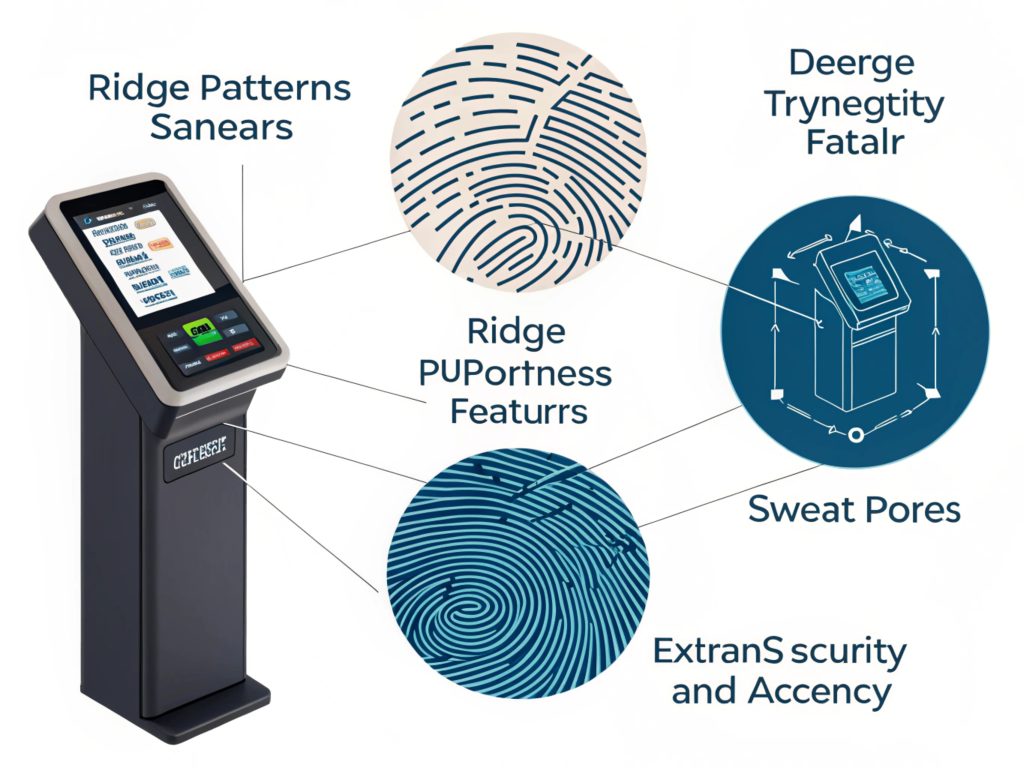
I switched to a biometric fingerprint scanner on my phone a year ago, and the difference was night and day. It worked perfectly even when my fingers were slightly sweaty or when I touched the scanner at odd angles. It’s a more advanced technology that recognizes finer details of my fingerprint.
How Biometric Fingerprint Scanners Work
Biometric fingerprint scanners often use ultrasonic waves or 3D imaging to scan the fingerprint in greater detail. Ultrasonic scanners create a 3D map of the fingerprint’s ridges and valleys, providing a far more accurate reading than traditional scanners.
| Biometric Fingerprint Scanner | Traditional Fingerprint Scanner |
| Uses ultrasonic or 3D imaging for better accuracy | Uses basic 2D image capturing |
| Works well in varying conditions (wet, dry fingers) | Struggles with dirt or damaged fingers |
| Almost impossible to spoof | Can be fooled with fake fingerprints |
Which One Should You Choose?
By now, you might be wondering which fingerprint scanner is better for you. Let’s break down the pros and cons to make the decision easier.
Both types have their uses, but biometric fingerprint scanners are generally the superior choice.
From my experience, if you’re looking for a scanner for everyday use—whether it’s for your phone, laptop, or office security—biometric scanners are simply better. They’re faster, more accurate, and more secure. But traditional scanners still have a place if you’re on a budget or only need basic security.
Biometric Fingerprint Scanners vs. Traditional: A Quick Comparison
| Factor | Traditional Fingerprint Scanner | Biometric Fingerprint Scanner |
| Security | Moderate | High |
| Accuracy | Low to Medium | High |
| Cost | Low to Medium | High |
| Speed | Moderate | Fast |
Conclusion
After comparing both types of fingerprint scanners, I believe biometric fingerprint scanners offer the best combination of security, accuracy, and convenience. While traditional scanners are still widely used, if you want more reliable protection, especially for sensitive applications, the biometric option is the way to go.
Traditional Fingerprint Scanners[^1]
[^1]: Understanding the mechanics behind Traditional Fingerprint Scanners can enhance your knowledge on biometric security systems.
Biometric Fingerprint Scanners[^1]
[^1]: Discover how Biometric Fingerprint Scanners offer a higher level of security by using unique biological characteristics, making unauthorized access nearly impossible.
3D Imaging Fingerprint Scanners[^1]
Fake Fingerprint Detection[^2]
[^1]: Discover how 3D imaging technology revolutionizes fingerprint scanning, offering unparalleled security and accuracy.
[^2]: Learn about cutting-edge technologies that detect and prevent fake fingerprint attempts, ensuring your security is foolproof.